文章目录
- 文本检测
- 文本识别
- CTC层
- 生成验证码并制作数据集
- 建立模型
- 模型推理
- 参考
文本检测
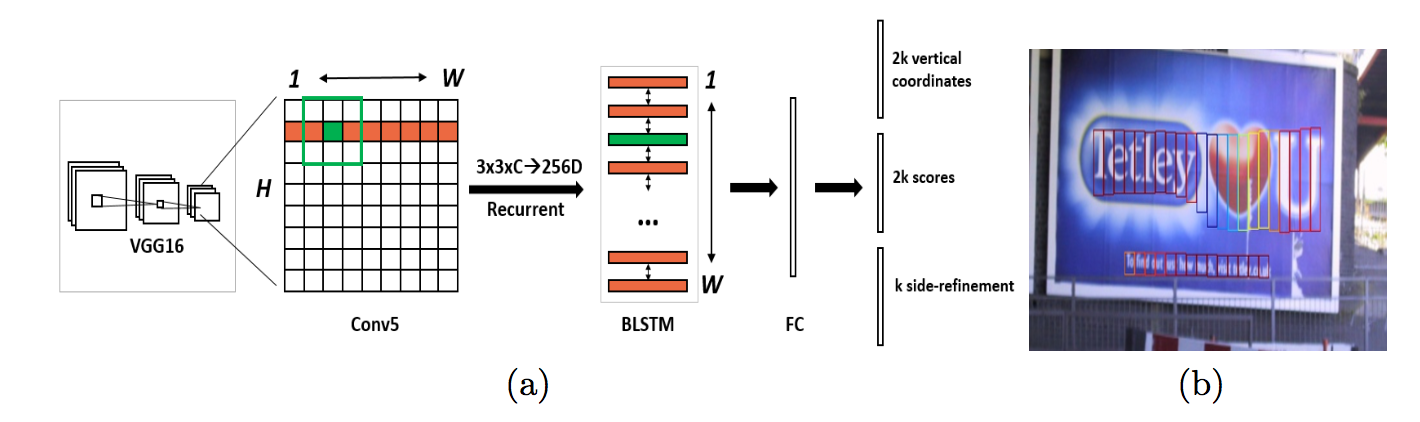
文本检测和目标检测类似,其不同之处在于文本目标具有序列特征,有连续性,可以通过结合 Faster R-CNN 和 LSTM 的方式进行文本检测,如 CTPN 网络,其网络结构来自论文: Detecting Text in Natural Image with Connectionist Text Proposal Network (arxiv.org);
CNN学习的是感受野内的空间信息,LSTM学习的是序列特征。对于文本序列检测,显然既需要CNN抽象空间特征,也需要序列特征(毕竟文字是连续的)。
详细可以查看场景文字检测—CTPN原理与实现 - 知乎 (zhihu.com),CTPN网络的缺点很明显,只能识别行排列文本,如果文本充满艺术排列效果就不是很好;
这里有其他更好的方法进行文本检测:
- FCENet:[2104.10442] Fourier Contour Embedding for Arbitrary-Shaped Text Detection (arxiv.org)
- DBNet:[1911.08947] Real-time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization (arxiv.org)
- DBNet++:[2202.10304] Real-Time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization and Adaptive Scale Fusion (arxiv.org)
详细介绍可以看这个网站:天天教程 (foobarweb.net)
文本识别
在检测到文本位置后,我们提取出文本图片,将文本图片转化为同一大小格式,接着我们需要执行将文本图片转化为字符串任务;
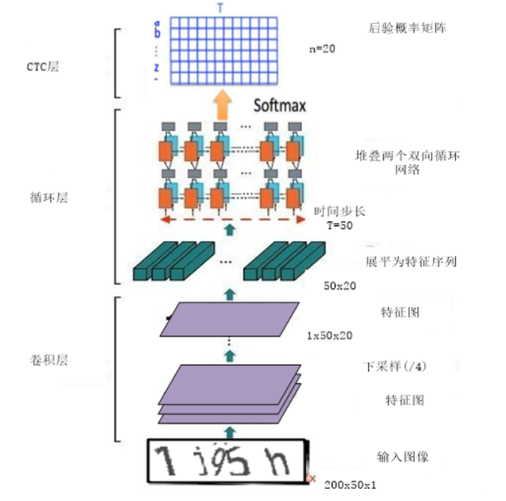
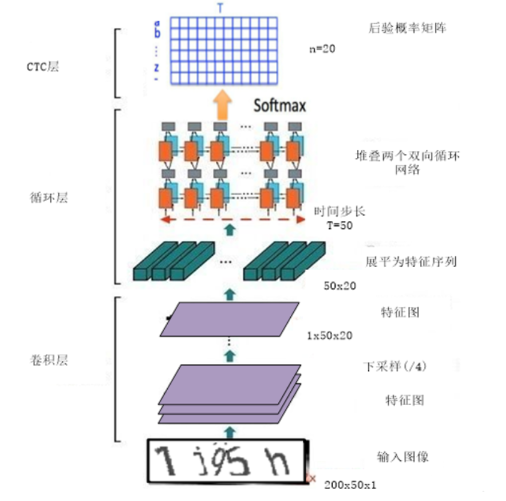
文章中使用的是 CNN+RNN+CTC(CRNN+CTC) 架构,具体如下图所示
CTC层
CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification),其被设计用来解决输入序列和输出序列难以一一对应的问题。
我们在特征图展开为特征序列这一步骤中,将原始特征图切割成不同的小块,理想情况是不同小块分别顺序对应目标字符串中某一字符,由于图片的无规则性以及感受野的存在,这种情况是不现实的,目标字符串中的字符很有可能被不同的块分别对应,这会导致字符串重复的情况出现,因此我们需要对齐预测序列和真实序列,Sequence Modeling with CTC (distill.pub)详细介绍了这一效果;
CTC 本质上是一个 softmax 矩阵,其 row nums 由预测的字符类别数量决定,其 col nums 又特征图切割成不同的小块的数量决定,这里 col nums 又称为时间步 T , 假设我们预测的字符串长度为 true_string_length ,由于每一时间步只能预测一个字符再加上空字符和重复字符的出现,我们必须要保证时间步 T 要大于 true_string_length ;
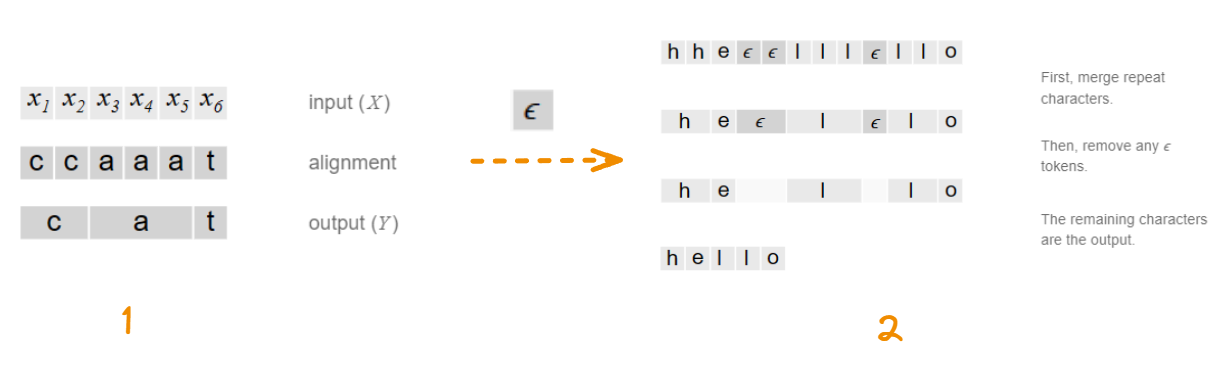
对重复字符进行删除,如下图1所示,这会导致两个问题:
- 通常,强制每个输入步骤与某些输出对齐是没有意义的。例如,在语音识别中,输入可能会出现一段沉默而没有相应的输出。
- 我们无法产生连续多个字符的输出。考虑对齐方式 [h, h, e, l, l, l, o]。折叠重复将产生“helo”而不是“hello”。
这里引入一个空字符: ϵ \epsilon ϵ,利用该字符去间隔重复字符,然后进行删除就可以解决上面两个问题,具体效果如上图2所示;
如何具体实施这一操作呢,这里我们可以对 y 进行处理,对 y 做一个简单的变换: π 0 = [ ϵ , y 1 , ϵ , y 2 , ϵ , … , y n , ϵ ] \pi_0=[\epsilon, y_1,\epsilon,y_2,\epsilon,\dots,y_n,\epsilon] π0=[ϵ,y1,ϵ,y2,ϵ,…,yn,ϵ]
得到其概率为 p ( π 0 ∣ X ) p(\pi_0|X) p(π0∣X),由于 y 的变换有很多,如果 y 1 y_1 y1 不等于 y 2 y_2 y2 ,那么有许多的新变换,如 π 1 = [ ϵ , y 1 , y 2 , ϵ , ϵ , … , y n , ϵ ] \pi_1=[\epsilon, y_1,y_2,\epsilon,\epsilon,\dots,y_n,\epsilon] π1=[ϵ,y1,y2,ϵ,ϵ,…,yn,ϵ] 等等
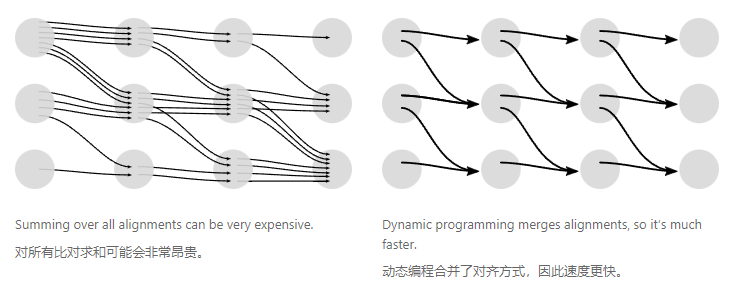
这里将所有的变换的概率值作为损失,得到损失如下: L = ∑ i − log p ( y i ∣ X i ) = ∑ i ∑ j − log p ( π i j ∣ X i ) \mathcal{L} = \sum_i -\log p(y_i|X_i)=\sum_i \sum_j-\log p(\pi_{ij}|X_i) L=i∑−logp(yi∣Xi)=i∑j∑−logp(πij∣Xi)
由于变换很多,单一计算非常困难,这里我们可以使用动态规划进行简化,详细请看:Sequence Modeling with CTC (distill.pub)
tensorflow 有 CTC 损失计算的接口,接口如下:
tf.nn.ctc_loss( labels, inputs, sequence_length, preprocess_collapse_repeated=False, ctc_merge_repeated=True, ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs=False, time_major=True )生成验证码并制作数据集
captcha 是 python 用来生成随机验证码的一个库,可以使用 pip install captcha 安装
定义两个函数 random_captcha_text ,gen_captcha_text_and_image 分别执行随机生成验证码文本和验证码图片生成任务;
import os import random from rich.progress import track from captcha.image import ImageCaptcha def random_captcha_text(char_set=None, captcha_size=5): """随机生成 number 和 alphabet 组合的字符串""" if char_set is None: number = [ '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'] alphabet = [ 'a', 'd', 'h', 'j', 'k', 'q', 's', 't', 'y'] char_set = number + alphabet captcha_text = [] for i in range(captcha_size): c = random.choice(char_set) captcha_text.append(c) return ''.join(captcha_text) def gen_captcha_text_and_image(width=200, height=50, char_set=None, save_path='./captcha_imgs/'): """随机生成验证码并保存在./captcha_imgs/文件目录下""" os.makedirs(save_path, exist_ok=True) ic = ImageCaptcha(width=width, height=height) captcha_text = random_captcha_text(char_set) img= ic.create_captcha_image(captcha_text,color='red', background='white') # create_noise_curve方法将上面生成的验证码 img 画上干扰线 img = ic.create_noise_curve(img, color='black') img.save(save_path+captcha_text+".png") return captcha_text, img利用 gen_captcha_text_and_image 生成3000个验证码图片作为数据集图片,下一步开始制作数据集
nums = 3000 for step in track(range(nums)): gen_captcha_text_and_image() # Working... ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 100% 0:00:14数据集制作
import os import random from pathlib import Path import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def process_data(img_path, label): """dataset --> process_dataset""" img = tf.io.read_file(img_path) img = tf.io.decode_png(img, channels=1) img = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img, tf.float32) label = tf.strings.unicode_split(label, input_encoding="UTF-8") label = char_num(label) # 固定 TensorSpec img = tf.reshape(img, [50, 200, 1]) label = tf.reshape(label, [5]) return img, label # 存储验证码文件夹 ./captcha_imgs/ data_dir = Path('./captcha_imgs/') image_paths = list(map(str, list(data_dir.glob("*.png")))) labels = [image_path.split(os.path.sep)[1].split('.png')[0] for image_path in image_paths] # image_paths[0], labels[0] --> ('captcha_imgs\\1113s.png', '1113s') characters = sorted(list(set(char for label in labels for char in label))) # ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'd', 'h', 'j', 'k', 'q', 's', 't', 'y'] # 定义两个转换,一个是将char转化为num,一个是将num转化为char char_num = tf.keras.layers.StringLookup(vocabulary=characters, invert=False) num_char = tf.keras.layers.StringLookup(vocabulary=characters, invert=True ) # 切割数据集 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(image_paths, labels, test_size=0.33, random_state=42) # 定义超参数 batch_size = 16 # 制作数据集 train_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X_train, y_train)) test_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X_test, y_test)) train_data = train_data.map(process_data).batch(batch_size).prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE).cache() test_data = test_data.map(process_data).batch(batch_size)可视化数据代码
def plot_16_images(): plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4)) imgs, labels = train_data.take(1).get_single_element() for ix in range(imgs.shape[0]): plt.subplot(4, 4, ix+1) plt.imshow(imgs[ix]) plt.title(tf.strings.reduce_join(num_char(labels[ix])).numpy().decode('utf-8')) plt.axis('off') plt.tight_layout() plt.show() plot_16_images()得到结果如下
建立模型
模型架构如图,现在使用代码实现该模型架构;
实现模型架构代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf class CustomModel(tf.keras.models.Model): def __init__(self): super(CustomModel, self).__init__() self.conv_1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu', padding='same') self.conv_2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same') self.max_pool_1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2)) self.max_pool_2 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2)) self.blstm_1 = tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(128, return_sequences=True, dropout=0.25)) self.blstm_2 = tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, return_sequences=True, dropout=0.25)) self.dense_1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu') self.dense_2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(len(characters) + 2, activation='softmax') self.dropout = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2) def call(self, x): x = tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3]) x = self.conv_1(x) x = self.max_pool_1(x) x = self.conv_2(x) x = self.max_pool_2(x) x = tf.reshape(x, [tf.shape(x)[0], tf.shape(x)[1], -1]) x = self.dense_1(x) x = self.dropout(x) x = self.blstm_1(x) x = self.blstm_2(x) x = self.dense_2(x) return x def custom_loss(y_true, y_pred): batch_len = tf.cast(tf.shape(y_true)[0], dtype="int64") input_length = tf.cast(tf.shape(y_pred)[1], dtype="int64") label_length = tf.cast(tf.shape(y_true)[1], dtype="int64") # 1 慢一些 # input_length = input_length * tf.ones(shape=(batch_len), dtype="int64") # label_length = label_length * tf.ones(shape=(batch_len), dtype="int64") # loss = tf.nn.ctc_loss(y_true, y_pred, label_length, input_length, logits_time_major=False) # 2 快一些 input_length = input_length * tf.ones(shape=(batch_len, 1), dtype="int64") label_length = label_length * tf.ones(shape=(batch_len, 1), dtype="int64") loss = tf.keras.backend.ctc_batch_cost(y_true, y_pred, input_length, label_length) return loss model = CustomModel() # build the model model(train_data.take(1).get_single_element()[0]) # summary the model model.summary()compile 模型并开始训练:
model.compile( optimizer='adam', loss=custom_loss ) model.fit(train_data, validation_data=test_data, epochs=200)得到训练过程如下:
Epoch 1/200 169/169 [==============================] - 21s 61ms/step - loss: 22.0665 - val_loss: 16.1782 Epoch 2/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 39ms/step - loss: 16.1598 - val_loss: 16.1217 ......................................................................................... 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 39ms/step - loss: 15.4558 - val_loss: 15.6200 Epoch 27/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 39ms/step - loss: 15.4595 - val_loss: 15.6041 Epoch 28/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 15.4209 - val_loss: 15.4314 Epoch 29/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 15.1606 - val_loss: 14.4924 Epoch 30/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 14.1823 - val_loss: 12.9583 Epoch 31/200 ......................................................................................... Epoch 42/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 0.6783 - val_loss: 0.2937 Epoch 43/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 0.6130 - val_loss: 0.2544 Epoch 44/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 39ms/step - loss: 0.4716 - val_loss: 0.2368 ......................................................................................... Epoch 194/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 0.0463 - val_loss: 0.1134 Epoch 195/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 0.0439 - val_loss: 0.0840 Epoch 196/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 41ms/step - loss: 0.0767 - val_loss: 0.1057 Epoch 197/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 41ms/step - loss: 0.0326 - val_loss: 0.0906 Epoch 198/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 41ms/step - loss: 0.0224 - val_loss: 0.0844 Epoch 199/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 41ms/step - loss: 0.0701 - val_loss: 0.1003 Epoch 200/200 169/169 [==============================] - 7s 40ms/step - loss: 0.0477 - val_loss: 0.0911
模型推理
当模型训练完毕后,模型的输出并不是目标字符串,仍然是一个 softmax 矩阵,因此我们需要对该矩阵继续进行操作;
当我们训练好一个RNN模型时,给定一个输入序列X,我们需要找到最可能的输出,也就是求解
Y ∗ = a r g m a x k P ( Y / X ) Y^*=\underset{k}{argmax} P(Y/X) Y∗=kargmaxP(Y/X)
求解最可能的输出有两种方案,一种是Greedy Search,第二种是Beam Search
- Greedy Search:每个时间片均取该时间片概率最高的节点作为输出
- Beam Search:Beam Search是寻找全局最优值和Greedy Search在查找时间和模型精度的一个折中。一个简单的beam search在每个时间片计算所有可能假设的概率,并从中选出最高的几个作为一组。然后再从这组假设的基础上产生概率最高的几个作为一组假设,依次进行,直到达到最后一个时间片。
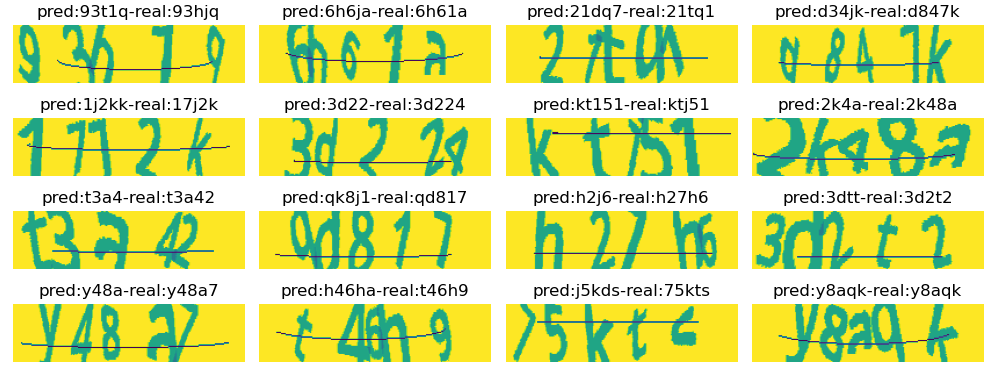
def decode_batch_predictions(X, mode='greedy'): """ mode 有两种模式 beam 和 greedy 一般来说 greedy 效果要好一些""" y_pred = model(X) if mode == 'beam': input_length = tf.cast(tf.shape(y_pred)[1], dtype="int64") zz = tf.nn.ctc_beam_search_decoder(tf.transpose(y_pred, perm=[1,0,2]), [50]*16)[0][0] zz = tf.strings.reduce_join(num_char(tf.sparse.to_dense(zz)), axis=-1).numpy() zz = [s.decode('utf-8').replace('[UNK]', '')[:5] for s in list(zz)] elif mode == 'greedy': input_length = tf.cast(tf.shape(y_pred)[1], dtype="int64") zz = tf.nn.ctc_greedy_decoder(tf.transpose(y_pred, perm=[1,0,2]), [50]*16)[0][0] zz = tf.strings.reduce_join(num_char(tf.sparse.to_dense(zz)), axis=-1).numpy() zz = [s.decode('utf-8').replace('[UNK]', '')[:5] for s in list(zz)] return zz可视化如下
def plot_16_images_pred(): plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4)) imgs, labels = test_data.take(1).get_single_element() pred_labels = decode_batch_predictions(imgs, mode='greedy') labels = [zz.decode('utf-8') for zz in tf.strings.reduce_join(num_char(labels), axis=-1).numpy()] for ix in range(imgs.shape[0]): plt.subplot(4, 4, ix+1) plt.imshow(imgs[ix]) plt.title(f'pred:{pred_labels[ix]}-real:{labels[ix]}') plt.axis('off') plt.tight_layout() plt.show() return pred_labels plot_16_images_pred()完毕!
参考
- 场景文字检测—CTPN原理与实现 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
- Detecting Text in Natural Image with Connectionist Text Proposal Network (arxiv.org)
- CTC Loss 数学原理讲解:Connectionist Temporal Classification-CSDN博客
- Sequence Modeling with CTC (distill.pub)
- 一文读懂CRNN+CTC文字识别 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
- CTC(Connectionist Temporal Classification)介绍 - PilgrimHui - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)



![[工业自动化-1]:PLC架构与工作原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ce10a1471ed14382bc58364cf8bd5209.png)





还没有评论,来说两句吧...