目录
1. 网站图书数据分析
2. 网站图书数据提取
3. 网站图书数据爬取
(1)创建 MySQL 数据库
(2)创建 scrapy 项目
(3)编写 items.py 中的数据项目类
(4)编写 pipelines_1.py 中的数据处理类
(5)编写 pipelines_2.py 中的数据处理类
(6)编写 Scrapy 的配置文件
(7)编写 Scrapy 爬虫程序
(8)执行 Scrapy 爬虫程序
实践内容:Scrapy框架+Xpath信息提取方法设计商城(这里用的当当网)商品信息网站及爬虫程序,以关键字“书包”(python)搜索页面的商品,爬取(学号相关的特定某几个页面(最后一位,页面大于3)及限定数量商品(最后3位))商品信息。
编程思路:
1. 功能描述
- 输入:需要爬取的商品与学号
- 输出:书本信息并保存的MySQL中
2. 程序的结构设计
- 从当当网上获取数据:使用scripy框架,使用xpath查找html元素
- 下面两个特定数量爬取写了两个管道 pipelines_1.py, pipelines_2.py
- 爬取1:(最后一位,页面大于3)——>(3,>3)并输出到MySQL中,open_scripy,把数据INSERT到数据库中,close_scripy
- 爬取2:(最后3位)——>103条数据,并输出到MySQL,open_scripy,把数据INSERT到数据库中,close_scripy
1. 网站图书数据分析
当当图书网站是国内比较大型的图书网站,这个项目的目的就是对该网站的某个主题的一类图书的数据的爬取,把爬取的数据存储到MySQL数据库中。
例如我们关心Python类的图书,想知道网站上有什么Python的图书,用 Chrome浏览器进入当当网站,在搜索关键字中输入"Python"搜索得到 Python的图书,地址转为:
http://search.dangdang.com/?key=Python&act=input
这类的图书很多,点击“下一页”后地址转为:
http://search.dangdang.com/?key=Python&act=input&page_index=2
从地址上我们知道知道搜索的关键字是key参数,页码参数是page_index, 而act=input参数只是表明是通过输入进行的查询。
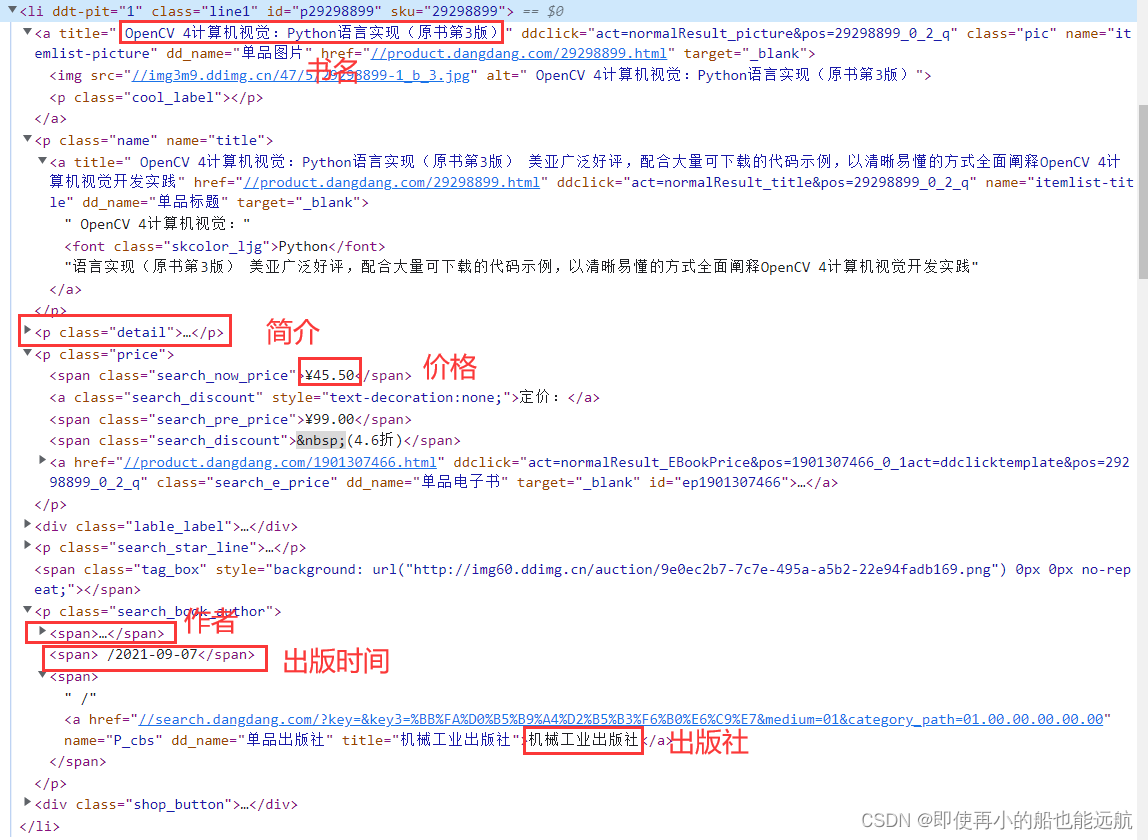
网页元素分析,为后面使用Xpath查找做准备
仔细分析 HTML 代码结构,可以看到每本书都是一个
- 的项目,而且它们的结构完全是一样的,这些
- 包含在一个
- 中。
- ,点击鼠标右键弹出菜单,执行"Edit as HTML" 进入文本编辑,复制出一本书
- 项目的代码,这段代码放到记事本中, 保存为book.txt文本文件时提示包含Unicode编码字符或者utf-16,于是按要求以 Unicode编码保存为book.txt文件。然后编写一小段程序用BeautifulSoup 装载:
BeautifulSoup 装载 Test1.py 如下:
# BeautifulSoup 装载 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup fobj = open("book.txt", "rb") data = fobj.read() fobj.close() data = data.decode("utf-16") soup = BeautifulSoup(data, "lxml") print(soup.prettify())通过 prettify 整理后就可以清晰看到
- 层次结构,结果如下:
Python
算法教程
精通Python基础算法 畅销书Python基础教程作者力作
¥51.75
定价:
¥69.00
(7.5折)
人民邮电出版社官方旗舰店
8条评论
[挪威]
Magnus
Lie
Hetland
赫特兰
/2016-01-01
/
人民邮电出版社
加入购物车
收藏
2. 网站图书数据提取
假定只关心图书的名称title、作者author、出版时间date、出版 社publisher、价格price以及书的内容简介detail,那么用book.txt存储的代码来测试获取的方法。从book.txt中的代码的分析,我们可以编写 test.py 程序获取这些数据.
图书数据获取 Test2.py 如下:
# 图书数据获取 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from bs4.dammit import UnicodeDammit import scrapy class TestItem: def __init__(self): self.title = "" self.author = "" self.date = "" self.publisher = "" self.price = "" self.detail = "" def show(self): print(self.title) print(self.author) print(self.date) print(self.price) print(self.publisher) print(self.detail) try: # 这段程序从book.txt中装载数据,并识别它的编码,生成Selector对象,并由此找到 - 元素节点。 fobj = open("book.txt", "rb") data = fobj.read() fobj.close() dammit = UnicodeDammit(data, ["utf-8", "utf-16", "gbk"]) data = dammit.unicode_markup selector = scrapy.Selector(text=data) li = selector.xpath("//li") #
- 中有多个,从HTML代码可以看到书名包含在第一个的title属性中, # 因此通过position()=1找出第一个,然后取出title属性值就是书名title。 title = li.xpath("./a[position()=1]/@title").extract_first() # 价钱包含在
- 中的class='price'的
元素下面的 class='search_now_price'的元素的文本中。 price = li.xpath("./p[@class='price']/span[@class='search_now_price']/text()").extract_first() # 作者包含在
- 下面的class='search_book_author'的
元素下面的第一个 # 元素的title属性中,其中span[position()=1]就是限定第一个 。 author = li.xpath("./p[@class='search_book_author']/span[position()=1]/a/@title").extract_first() # 出版日期包含在
- 下面的class='search_book_author'的
元素下面的倒数第二个元素的文本中, # 其中span[position()=last()-1]就是限定倒数第二个 ,last()是最后一个的序号。 date = li.xpath("./p[@class='search_book_author']/span[position()=last()-1] / text()").extract_first() # 出版社包含在
- 下面的class='search_book_author'的
元素下面的最 后一个元素的title属性中, # 其中span[position()=last()]就是最后一 个 ,last()是最后一个的序号。 publisher = li.xpath("./p[@class='search_book_author']/span[position()=last()]/a/@title").extract_first() # 在
- 下面的class='detail'的
的文本就是书的简介。 detail = li.xpath("./p[@class='detail']/text()").extract_first() item = TestItem() # 无论是哪个数据存在, 那么extract_first()就返回这个数据的值, # 如果不存在就返回None,为了避免出现None的值,我们把None转为空字符串。 item.title = title.strip() if title else "" item.author = author.strip() if author else "" # 从HTML中看到日期前面有一个符号"/",因此如果日期存在时就把这个前导的符号"/"去掉。 item.date = date.strip()[1:] if date else "" item.publisher = publisher.strip() if publisher else "" item.price = price.strip() if price else "" item.detail = detail.strip() if detail else "" item.show() except Exception as err: print(err)
程序执行结果:
Python 算法教程
[挪威] Magnus Lie Hetland 赫特兰
2016-01-01
¥51.75
人民邮电出版社
精通Python基础算法 畅销书Python基础教程作者力作
3. 网站图书数据爬取
(1)创建 MySQL 数据库
注意:下面创建数据库与数据表,已在 pipelines.py 中编写了
在 MySQL 中创建数据库 scripy, 创建2个图书表books如下:
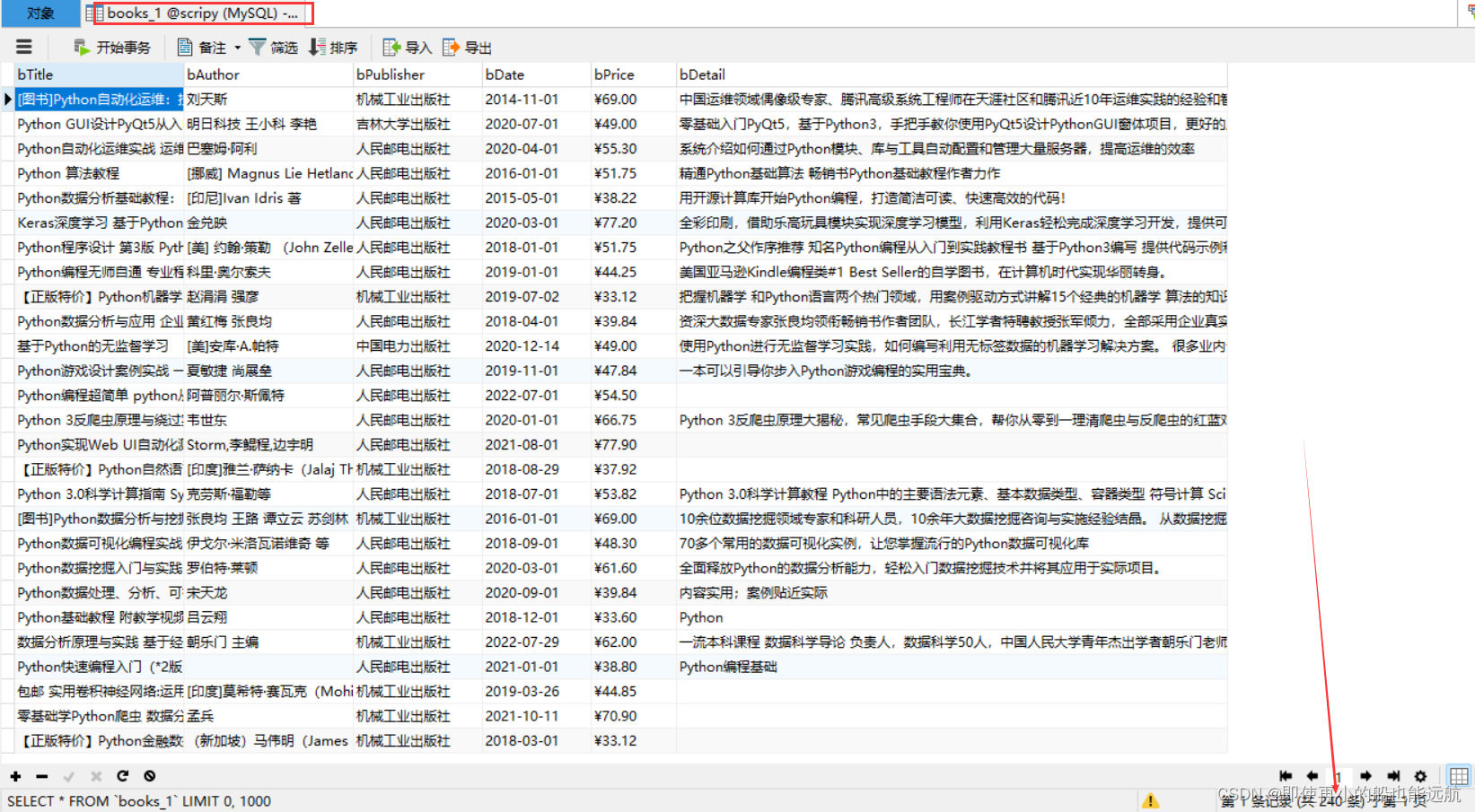
CREATE DATABASE scripy; CREATE TABLE books( bTitle VARCHAR(512), bAuthor VARCHAR(256), bPublisher VARCHAR(256), bDate VARCHAR(32), bPrice VARCHAR(16), bDetail text );(2)创建 scrapy 项目
scrapy startproject Project_books
(3)编写 items.py 中的数据项目类
# Define here the models for your scraped items # # See documentation in: # https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class BookItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: title = scrapy.Field() author = scrapy.Field() date = scrapy.Field() publisher = scrapy.Field() detail = scrapy.Field() price = scrapy.Field()(4)编写 pipelines_1.py 中的数据处理类
# Define your item pipelines here # # Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html # useful for handling different item types with a single interface import pymysql class BookPipeline(object): def open_spider(self, spider): print("opened_爬取1") try: self.con = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', password="123456", charset="utf8") self.cursor = self.con.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) self.cursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS scripy") self.con = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', password="123456", db='scripy', charset="utf8") self.cursor = self.con.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) self.cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS books_1(" "bTitle VARCHAR(512)," "bAuthor VARCHAR(256)," "bPublisher VARCHAR(256)," "bDate VARCHAR(32)," "bPrice VARCHAR(16)," "bDetail text)") self.cursor.execute("DELETE FROM books_1") self.opened = True self.count_1 = 0 except Exception as err: print(err) self.opened = False def close_spider(self, spider): if self.opened: self.con.commit() self.con.close() self.opened = False print("closed_爬取1") print(f"总共爬取{self.count_1}本书籍") def process_item(self, item, spider): try: print(item["title"]) print(item["author"]) print(item["publisher"]) print(item["date"]) print(item["price"]) print(item["detail"]) print() if self.opened: self.cursor.execute("INSERT INTO books_1(bTitle,bAuthor,bPublisher,bDate,bPrice,bDetail)" "value (%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)", (item["title"], item["author"], item["publisher"], item["date"], item["price"], item["detail"])) self.count_1 += 1 except Exception as err: print(err) # spider.crawler.engine.close_spider(spider, "无有效信息,关闭spider") # pepline 中使用此关闭方法 return item(5)编写 pipelines_2.py 中的数据处理类
# Define your item pipelines here # # Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html # useful for handling different item types with a single interface import pymysql class Input_message: key = input('请输入需要爬取当当网的某类书籍:') id = input("请输入学号:") # 102002103 page = id[-1] # 爬取1-->第3页开始,爬取大于3页结束 page_1 = int(input(f"从第{page}开始,爬取__页(请大于3页):")) num = id[-3:] # 爬取2-->103件商品 class BookPipeline(object): def open_spider(self, spider): print("opened_爬取2") try: self.con = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', password="123456", charset="utf8") self.cursor = self.con.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) self.cursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS scripy") self.con = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', password="123456", db='scripy', charset="utf8") self.cursor = self.con.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) self.cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS books_2(" "bTitle VARCHAR(512)," "bAuthor VARCHAR(256)," "bPublisher VARCHAR(256)," "bDate VARCHAR(32)," "bPrice VARCHAR(16)," "bDetail text)") self.cursor.execute("DELETE FROM books_2") self.opened = True self.count_2 = 0 except Exception as err: print(err) self.opened = False def close_spider(self, spider): if self.opened: self.con.commit() self.con.close() self.opened = False print("closed_爬取2") print(f"总共爬取{self.count_2}本书籍") def process_item(self, item, spider): try: print(item["title"]) print(item["author"]) print(item["publisher"]) print(item["date"]) print(item["price"]) print(item["detail"]) print() if self.opened: self.cursor.execute("INSERT INTO books_2(bTitle,bAuthor,bPublisher,bDate,bPrice,bDetail)" "value (%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)", (item["title"], item["author"], item["publisher"], item["date"], item["price"], item["detail"])) self.count_2 += 1 if self.count_2 == int(Input_message.num): # 学号后3为 BookPipeline.close_spider(self, spider) except Exception as err: print(err) # spider.crawler.engine.close_spider(spider, "无有效信息,关闭spider") # pepline 中使用此关闭方法 return item在scrapy的过程中一旦打开一个 spider 爬虫, 就会执行这个类的 open_spider(self,spider) 函数,一旦这个 spider 爬虫关闭, 就执行这个类的 close_spider(self,spider) 函数。因此程序在open_spider 函数中连接 MySQL数据库,并创建操作游标 self.cursor,在close_spider中提交数 据库并关闭数据库,程序中使用 count 变量统计爬取的书籍数量。 在数据处理函数中每次有数据到达,就显示数据内容,并使用 insert 的SQL语句把数据插入到数据库中。
(6)编写 Scrapy 的配置文件settings.py
ITEM_PIPELINES = { "Project_books.pipelines_1.BookPipeline": 300, "Project_books.pipelines_2.BookPipeline": 300, }简单的配置 settings,这样就可以把爬取的数据推送到管道的BookPipeline类中。
(7)编写 Scrapy 爬虫程序MySpider.py
import scrapy from ..items import BookItem from bs4.dammit import UnicodeDammit from ..pipelines_2 import Input_message class MySpider(scrapy.Spider): name = "mySpider" source_url = "https://search.dangdang.com/" act = '&act=input&page_index=' # 以下信息写道pipelines2里了 # id = input("请输入学号:") # 102002103 # page = id[-1] # 爬取1-->第3页开始,爬取大于3页结束 # page_1 = int(input(f"从第{page}开始,爬取__页(请大于3页):")) # num = id[-3:] # 爬取2-->103件商品 # 指明要爬取的网址 def start_requests(self): # url = 'http://search.dangdang.com/?key=Python&act=input&page_index=2' url = MySpider.source_url + "?key=" + Input_message.key + MySpider.act + Input_message.page yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.parse) # 回调函数 def parse(self, response, **kwargs): try: dammit = UnicodeDammit(response.body, ["utf-8", "gbk"]) data = dammit.unicode_markup selector = scrapy.Selector(text=data) lis = selector.xpath("//li['@ddt-pit'][starts-with(@class,'line')]") for li in lis: title = li.xpath("./a[position()=1]/@title").extract_first() price = li.xpath("./p[@class='price']/span[@class='search_now_price']/text()").extract_first() author = li.xpath("./p[@class='search_book_author']/span[position()=1]/a/@title").extract_first() date = li.xpath("./p[@class='search_book_author']/span[position()=last()-1]/text()").extract_first() publisher = li.xpath( "./p[@class='search_book_author']/span[position()=last()]/a/@title").extract_first() detail = li.xpath("./p[@class='detail']/text()").extract_first() # detail 有时没有,结果None item = BookItem() item["title"] = title.strip() if title else "" item["author"] = author.strip() if author else "" item["date"] = date.strip()[1:] if date else "" item["publisher"] = publisher.strip() if publisher else "" item["price"] = price.strip() if price else "" item["detail"] = detail.strip() if detail else "" yield item # 最后一页时 link 为None # 1.连续爬取不同的页 # link = selector.xpath("//div[@class='paging']/ul[@name='Fy']/li[@class='next']/a/@href").extract_first() # if link: # url = response.urljoin(link) # yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.parse) # 2.翻页(学号最后一位+1,学号最后一位+input > 3) for i in range(int(Input_message.page) + 1, int(Input_message.page) + Input_message.page_1): url = MySpider.source_url + "?key=" + Input_message.key + MySpider.act + str(i) yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse) except Exception as err: print(err)分析网站的HTML代码发现在一个 的元素中包含了翻页的 信息,下面的
- 下面的
- 下面的 链接就是 下一页的链接,取出这个链接地址,通过 response.urljoin 函数整理成绝对地址,再次产生一个scrapy.Request对象请求,回调函数仍然为这个parse函数,这样就可以 递归调用parse函数,实现下一个网页的数据爬取。爬取到最后一页时,下一页的链接为空,link=None就不再递归调用了。
(8)执行 Scrapy 爬虫程序run.py
from scrapy import cmdline cmdline.execute("scrapy crawl mySpider -s LOG_ENABLED=False".split())执行这个程序就可以爬取到所有关于 xxx 的书籍,这些书籍的数据存储到MySQL的scripy数据库中,执行完毕后在MySQL中可以看到爬取的结果,产生了两张表,对应不同的数量要求。
控制台结果如下:
数据库结果如下:
总结:
scrapy把数据爬取与数据存储分开处理,它们都是异步执行的, MySpider每爬取到一个数据项目item,就yield推送给pipelines.py 程序存储,等待存储完毕后又再次爬取另外一个数据项目item,再次yield推送到pipelines.py程序,然后再次存储,......,这个过程一 直进行下去,直到爬取过程结束,文件books.txt中就存储了所有的 爬取数据了。
恭喜你成功突破第四章!人生不可能一帆风顺,逆境中更要坚定信念!
下一篇文章:5.1 商城网站项目背景与目标
实战源码:Python网络爬虫实战
- 下面的 链接就是 下一页的链接,取出这个链接地址,通过 response.urljoin 函数整理成绝对地址,再次产生一个scrapy.Request对象请求,回调函数仍然为这个parse函数,这样就可以 递归调用parse函数,实现下一个网页的数据爬取。爬取到最后一页时,下一页的链接为空,link=None就不再递归调用了。
在代码中选择第一个






![[工业自动化-1]:PLC架构与工作原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ce10a1471ed14382bc58364cf8bd5209.png)






还没有评论,来说两句吧...