seq2seq介绍
Seq2Seq(Sequence-to-Sequence)模型是一种在自然语言处理(NLP)中广泛应用的架构,其核心思想是将一个序列作为输入,并输出另一个序列。这种模型特别适用于机器翻译、聊天机器人、自动文摘等场景,其中输入和输出的长度都是可变的。
- embedding层在seq2seq模型中起着将离散单词转换为连续向量表示的关键作用,为后续的自然语言处理任务提供了有效的特征输入。
数据集
下载: https://download.pytorch.org/tutorial/data.zip
🍸️步骤:
基于GRU的seq2seq模型架构实现翻译的过程:
- 导入必备的工具包.
- 对文件中数据进行处理,满足模型训练要求.
- 构建基于GRU的编码器和解码
- 构建模型训练函数,并进行训练
- 构建模型评估函数,并进行测试以及Attention效果分析
# 从io工具包导入open方法 from io import open # 用于字符规范化 import unicodedata # 用于正则表达式 import re # 用于随机生成数据 import random # 用于构建网络结构和函数的torch工具包 import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F # torch中预定义的优化方法工具包 from torch import optim # 设备选择, 我们可以选择在cuda或者cpu上运行你的代码 device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")数据预处理
将指定语言中的词汇映射成数值💫
# 起始标志 SOS_token = 0 # 结束标志 EOS_token = 1 class Lang: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name self.word2index = {} self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"} self.n_words = 2 def addSentence(self, sentence): for word in sentence.split(' '): self.addWord(word) def addWord(self, word): if word not in self.word2index: self.word2index[word] = self.n_words self.index2word[self.n_words] = words self.n_words += 1- 测试:实例化参数:
name = "eng" sentence = "hello I am Jay" engl = Lang(name) engl.addSentence(sentence) print("word2index:", engl.word2index) print("index2word:", engl.index2word) print("n_words:", engl.n_words) # 输出 word2index: {'hello': 2, 'I': 3, 'am': 4, 'Jay': 5} index2word: {0: 'SOS', 1: 'EOS', 2: 'hello', 3: 'I', 4: 'am', 5: 'Jay'} n_words: 6字符规范化💫
def unicodeToAscii(s): return ''.join( c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s) if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn' ) def normalizeString(s): s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip()) s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s) s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s) return s将文件中的数据加载到内存,实例化类Lang💫
data_path = 'eng-fra.txt' def readLangs(lang1, lang2): """读取语言函数, 参数lang1是源语言的名字, 参数lang2是目标语言的名字 返回对应的class Lang对象, 以及语言对列表""" # 从文件中读取语言对并以/n划分存到列表lines中 lines = open(data_path, encoding='utf-8').read().strip().split('\n') # 对lines列表中的句子进行标准化处理,并以\t进行再次划分, 形成子列表, 也就是语言对 pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines] # 然后分别将语言名字传入Lang类中, 获得对应的语言对象, 返回结果 input_lang = Lang(lang1) output_lang = Lang(lang2) return input_lang, output_lang, pairs- 测试:输入参数:
lang1 = "eng" lang2 = "fra" input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2) print("pairs中的前五个:", pairs[:5]) # 输出 pairs中的前五个: [['go .', 'va !'], ['run !', 'cours !'], ['run !', 'courez !'], ['wow !', 'ca alors !'], ['fire !', 'au feu !']]过滤出符合我们要求的语言对💫
# 设置组成句子中单词或标点的最多个数 MAX_LENGTH = 10 eng_prefixes = ( "i am ", "i m ", "he is", "he s ", "she is", "she s ", "you are", "you re ", "we are", "we re ", "they are", "they re " ) def filterPair(p): return len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \ p[0].startswith(eng_prefixes) and \ len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH def filterPairs(pairs): return [pair for pair in pairs if filterPair(pair)]对以上数据准备函数进行整合💫
def prepareData(lang1, lang2): input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2) pairs = filterPairs(pairs) for pair in pairs: input_lang.addSentence(pair[0]) output_lang.addSentence(pair[1]) return input_lang, output_lang, pairs将语言对转化为模型输入需要的张量💫
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence): indexes = [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')] indexes.append(EOS_token) return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1) def tensorsFromPair(pair): input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0]) target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1]) return (input_tensor, target_tensor)- 测试输入:
# 取pairs的第一条 pair = pairs[0] pair_tensor = tensorsFromPair(pair) print(pair_tensor) # 输出 (tensor([[2], [3], [4], [1]]), tensor([[2], [3], [4], [5], [1]]))构建编码器和解码器
构建基于GRU的编码器
- “embedding”指的是一个将离散变量(如单词、符号等)转换为连续向量表示的过程或技术
- “embedded”是embedding过程的输出,即已经通过嵌入矩阵转换后的连续向量。在神经网络中,这些向量将作为后续层的输入。
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size): super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size) def forward(self, input, hidden): output = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1) output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) return output, hidden def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)- 测试:参数:
hidden_size = 25 input_size = 20 # pair_tensor[0]代表源语言即英文的句子,pair_tensor[0][0]代表句子中 的第一个词 input = pair_tensor[0][0] # 初始化第一个隐层张量,1x1xhidden_size的0张量 hidden = torch.zeros(1, 1, hidden_size) encoder = EncoderRNN(input_size, hidden_size) encoder_output, hidden = encoder(input, hidden) print(encoder_output) # 输出 tensor([[[ 1.9149e-01, -2.0070e-01, -8.3882e-02, -3.3037e-02, -1.3491e-01, -8.8831e-02, -1.6626e-01, -1.9346e-01, -4.3996e-01, 1.8020e-02, 2.8854e-02, 2.2310e-01, 3.5153e-01, 2.9635e-01, 1.5030e-01, -8.5266e-02, -1.4909e-01, 2.4336e-04, -2.3522e-01, 1.1359e-01, 1.6439e-01, 1.4872e-01, -6.1619e-02, -1.0807e-02, 1.1216e-02]]], grad_fn=) 构建基于GRU的解码器
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size): super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size) self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size) self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) def forward(self, input, hidden): output = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1) output = F.relu(output) output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) output = self.softmax(self.out(output[0])) return output, hidden def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)构建基于GRU和Attention的解码器💥
💥三个输入:
- prev_hidden:指上一个时间步解码器的隐藏状态
- input:input 是当前时间步解码器的输入。在解码的开始阶段,它可能是一个特殊的起始符号。在随后的解码步骤中,input 通常是上一个时间步解码器输出的词(或对应的词向量)。
- encoder_outputs :是编码器处理输入序列后生成的一系列输出向量,在基于Attention的解码器中,这些输出向量将作为注意力机制的候选记忆单元,用于计算当前解码步与输入序列中不同位置的相关性。
class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, dropout_p=0.1, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.dropout_p = dropout_p self.max_length = max_length self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.output_size, self.hidden_size) self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.max_length) self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(self.dropout_p) self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size) self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.output_size) def forward(self, input, hidden, encoder_outputs): embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1) embedded = self.dropout(embedded) attn_weights = F.softmax( self.attn(torch.cat((embedded[0], hidden[0]), 1)), dim=1) attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0), encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0)) output = torch.cat((embedded[0], attn_applied[0]), 1) output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0) output = F.relu(output) output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(output[0]), dim=1) return output, hidden, attn_weights def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)构建模型训练函数
teacher_forcing介绍
Teacher Forcing是一种在训练序列生成模型,特别是循环神经网络(RNN)和序列到序列(seq2seq)模型时常用的技术。在seq2seq架构中,根据循环神经网络理论,解码器每次应该使用上一步的结果作为输入的一部分, 但是训练过程中,一旦上一步的结果是错误的,就会导致这种错误被累积,无法达到训练效果,我们需要一种机制改变上一步出错的情况,因为训练时我们是已知正确的输出应该是什么,因此可以强制将上一步结果设置成正确的输出, 这种方式就叫做teacher_forcing。
teacher_forcing的作用
- 加速模型收敛与稳定训练:通过使用真实的历史数据作为解码器的输入,Teacher Forcing技术可以加速模型的收敛速度,并使得训练过程更加稳定,因为它避免了因模型早期预测错误而导致的累积误差。
- 矫正预测并避免误差放大:Teacher Forcing在训练时能够矫正模型的预测,防止在序列生成过程中误差的进一步放大,从而提高了模型的预测准确性。
# 设置teacher_forcing比率为0.5 teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5 def train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden() encoder_optimizer.zero_grad() decoder_optimizer.zero_grad() input_length = input_tensor.size(0) target_length = target_tensor.size(0) encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device) loss = 0 for ei in range(input_length): encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder( input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden) encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0] decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False if use_teacher_forcing: for di in range(target_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder( decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs) loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di]) decoder_input = target_tensor[di] else: for di in range(target_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder( decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs) topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1) loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di]) if topi.squeeze().item() == EOS_token: break decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # 误差进行反向传播 loss.backward() # 编码器和解码器进行优化即参数更新 encoder_optimizer.step() decoder_optimizer.step() # 返回平均损失 return loss.item() / target_length构建时间计算函数
import time import math def timeSince(since): now = time.time() # 获得时间差 s = now - since # 将秒转化为分钟 m = math.floor(s / 60) s -= m * 60 return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)调用训练函数并打印日志和制图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def trainIters(encoder, decoder, n_iters, print_every=1000, plot_every=100, learning_rate=0.01): start = time.time() plot_losses = [] print_loss_total = 0 plot_loss_total = 0 encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) criterion = nn.NLLLoss() for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1): training_pair = tensorsFromPair(random.choice(pairs)) input_tensor = training_pair[0] target_tensor = training_pair[1] loss = train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion) print_loss_total += loss plot_loss_total += loss if iter % print_every == 0: print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every print_loss_total = 0 print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (timeSince(start), iter, iter / n_iters * 100, print_loss_avg)) if iter % plot_every == 0: plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg) plot_loss_total = 0 plt.figure() plt.plot(plot_losses) plt.savefig("loss.png")💥训练模型:
# 设置隐层大小为256 ,也是词嵌入维度 hidden_size = 256 # 通过input_lang.n_words获取输入词汇总数,与hidden_size一同传入EncoderRNN类中 # 得到编码器对象encoder1 encoder1 = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device) # 通过output_lang.n_words获取目标词汇总数,与hidden_size和dropout_p一同传入AttnDecoderRNN类中 # 得到解码器对象attn_decoder1 attn_decoder1 = AttnDecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, dropout_p=0.1).to(device) # 设置迭代步数 n_iters = 80000 # 设置日志打印间隔 print_every = 5000 trainIters(encoder1, attn_decoder1, n_iters, print_every=print_every)
模型会不断打印loss损失值并且绘制图像
- 一直下降的损失曲线, 说明模型正在收敛
构建模型评估函数
def evaluate(encoder, decoder, sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): with torch.no_grad(): # 对输入的句子进行张量表示 input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence) # 获得输入的句子长度 input_length = input_tensor.size()[0] encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden() encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device) for ei in range(input_length): encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden) encoder_outputs[ei] += encoder_output[0, 0] decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden decoded_words = [] # 初始化attention张量 decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length) # 开始循环解码 for di in range(max_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder( decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs) decoder_attentions[di] = decoder_attention.data topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1) if topi.item() == EOS_token: decoded_words.append('') break else: decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi.item()]) decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() return decoded_words, decoder_attentions[:di + 1] 随机选择指定数量的数据进行评估
def evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder, n=6): for i in range(n): pair = random.choice(pairs) # > 代表输入 print('>', pair[0]) # = 代表正确的输出 print('=', pair[1]) # 调用evaluate进行预测 output_words, attentions = evaluate(encoder, decoder, pair[0]) # 将结果连成句子 output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words) # < 代表模型的输出 print('<', output_sentence) print('') evaluateRandomly(encoder1, attn_decoder1)效果:
> i m impressed with your french . = je suis impressionne par votre francais . < je suis impressionnee par votre francais .
> i m more than a friend . = je suis plus qu une amie . < je suis plus qu une amie . > she is beautiful like her mother . = elle est belle comme sa mere . < elle est sa sa mere . > you re winning aren t you ? = vous gagnez n est ce pas ? < tu restez n est ce pas ? > he is angry with you . = il est en colere apres toi . < il est en colere apres toi . > you re very timid . = vous etes tres craintifs . < tu es tres craintive . Attention张量制图
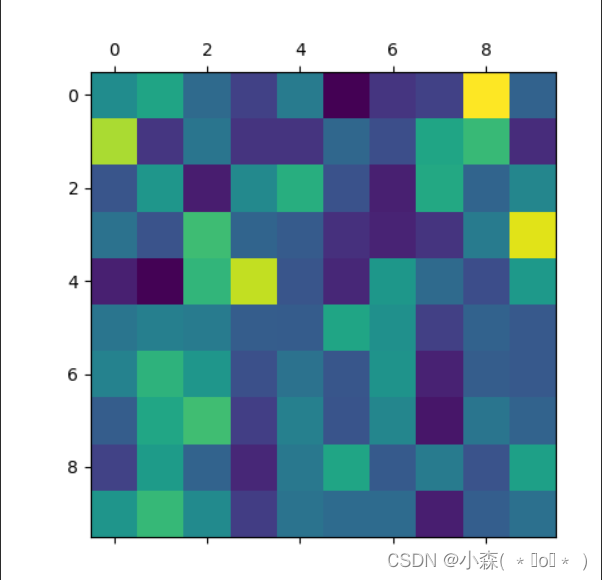
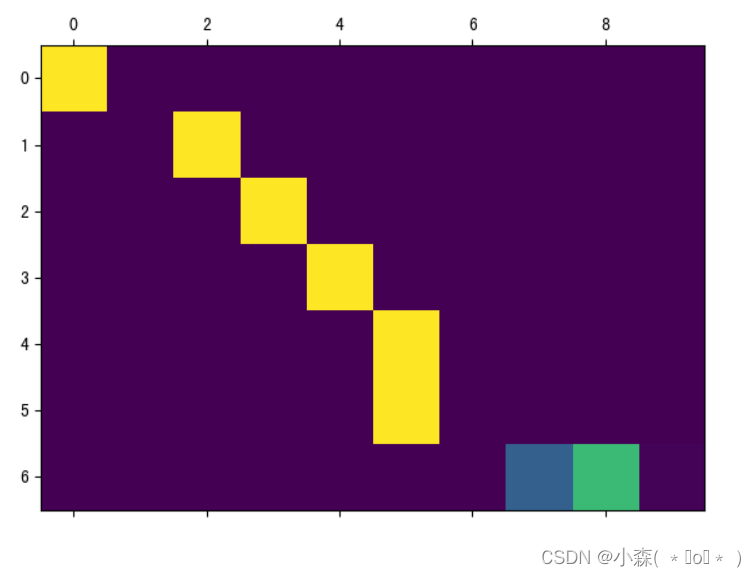
sentence = "we re both teachers ." # 调用评估函数 output_words, attentions = evaluate( encoder1, attn_decoder1, sentence) print(output_words) # 将attention张量转化成numpy, 使用matshow绘制 plt.matshow(attentions.numpy()) plt.savefig("attn.png")如果迭代次数过少,训练不充分,那么注意力就不会很好:
💯迭代次数变大:
- 一直下降的损失曲线, 说明模型正在收敛
- 测试:参数:
- 测试输入:
- 测试:输入参数:
- 测试:实例化参数:










![[工业自动化-1]:PLC架构与工作原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ce10a1471ed14382bc58364cf8bd5209.png)






还没有评论,来说两句吧...