XML语法规则介绍及总结-CSDN博客
TinyXML-2 是一个简单轻量级的 C++ XML 解析库,它提供了一种快速、高效地解析 XML 文档的方式。
1. 下载地址
Gitee 极速下载/tinyxml2
2. 基本用法
下面将详细介绍 TinyXML-2 的主要使用方法:
2.1. 引入头文件和命名空间
#include "tinyxml2.h" using namespace tinyxml2;
2.2. 解析 XML 文档
XMLDocument doc;
doc.LoadFile("example.xml");
if (doc.ErrorID() != XML_SUCCESS) {
// 处理错误
return;
}
2.3. 访问根节点
XMLElement* root = doc.RootElement();
2.4. 遍历子节点
for (XMLElement* elem = root->FirstChildElement(); elem; elem = elem->NextSiblingElement()) {
// 处理节点
}
2.5. 读取节点属性
const char* attr = elem->Attribute("name");
if (attr) {
// 处理属性值
}
2. 6. 读取节点文本内容
const char* text = elem->GetText();
if (text) {
// 处理文本内容
}
2.7. 除了遍历和读取节点,TinyXML-2 还提供了丰富的节点操作 API,包括创建、插入、删除、克隆节点等。
// 创建新节点并插入到现有节点下
XMLElement* newElem = doc.NewElement("new_element");
root->InsertEndChild(newElem);
// 删除节点
root->DeleteChild(newElem);
// 克隆节点
XMLElement* clonedElem = newElem->DeepClone(&doc);
root->InsertEndChild(clonedElem);
2.8. 创建新节点并添加到文档
XMLElement* newElem = doc.NewElement("new_element");
newElem->SetAttribute("attribute", "value");
newElem->SetText("New element text");
root->InsertEndChild(newElem);
2.9. 文档操作
TinyXML-2 不仅可以解析现有的 XML 文档,还可以创建新的 XML 文档,并进行保存和打印操作。
// 创建新文档
XMLDocument doc;
XMLDeclaration* decl = doc.NewDeclaration();
doc.InsertFirstChild(decl);
XMLElement* root = doc.NewElement("root");
doc.InsertEndChild(root);
// 保存文档
doc.SaveFile("new_document.xml");
// 打印文档
doc.Print();
2.10. 保存 XML 文档
doc.SaveFile("new_example.xml");
2.11. 错误处理
TinyXML-2 提供了丰富的错误处理机制。您可以通过检查 doc.ErrorID() 和 doc.ErrorName() 来获取错误编号和错误信息。
if (doc.ErrorID() != XML_SUCCESS) {
printf("Error loading file: %s\n", doc.ErrorName());
return;
}
2.12.内存管理
TinyXML-2 使用自己的内存管理机制,无需手动分配和释放内存。所有的内存分配和释放都由库内部完成。
3. 代码示例
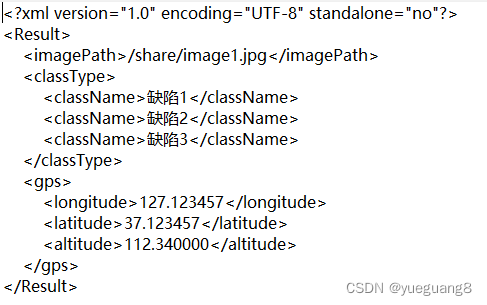
生成一个xml,用于保存照片路径,GPS信息及缺陷信息等。
#include "tinyxml2.h" #includeusing namespace tinyxml2; int SaveInfo(std::string xmlFile, std::string imagePath, std::string *calssName, int calssNameNum, double lon, double lat, double alt) { XMLDocument* doc = new XMLDocument(); if(doc == NULL) { printf("New xml is NULL!\n"); return -1; } if(xmlFile.empty()) { printf("xmlFile path is NULL!\n"); return -1; } // 创建xml const char* declaration =""; doc->Parse(declaration);//会覆盖xml所有内容 //创建根目录 XMLElement* root = doc->NewElement("Result"); doc->InsertEndChild(root); //路径 XMLElement* imagePathNode = doc->NewElement("imagePath"); imagePathNode->InsertEndChild(doc->NewText(imagePath.c_str())); root->InsertEndChild(imagePathNode); //缺陷类别 XMLElement* classTypeNode = doc->NewElement("classType"); for(int i = 0; i < calssNameNum; i++) { XMLElement* classNameNode = doc->NewElement("className"); XMLText* classNameText=doc->NewText(calssName[i].c_str()); classNameNode->InsertEndChild(classNameText); classTypeNode->InsertEndChild(classNameNode); } root->InsertEndChild(classTypeNode); //经度 XMLElement* gpsNode = doc->NewElement("gps"); XMLElement* longitudeNode = doc->NewElement("longitude"); XMLText* lonText=doc->NewText(std::to_string(lon).c_str()); longitudeNode->InsertEndChild(lonText); //纬度 XMLElement* latitudeNode = doc->NewElement("latitude"); XMLText* latText=doc->NewText(std::to_string(lat).c_str()); latitudeNode->InsertEndChild(latText); //高度 XMLElement* altitudeNode = doc->NewElement("altitude"); XMLText* altText=doc->NewText(std::to_string(alt).c_str()); altitudeNode->InsertEndChild(altText); gpsNode->InsertEndChild(longitudeNode); gpsNode->InsertEndChild(latitudeNode); gpsNode->InsertEndChild(altitudeNode); root->InsertEndChild(gpsNode); if(XML_SUCCESS != doc->SaveFile((char *)xmlFile.c_str())) { printf("ERROR: Save xml:%s fail\n", xmlFile.c_str()); doc->PrintError(); return -1; } printf("Save xmlFile success!\n"); return 0; }
运行结果:
4. 总结
TinyXML-2 是一个功能强大、易用的 XML 解析库,适合各种 C++ 项目使用


![[工业自动化-1]:PLC架构与工作原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ce10a1471ed14382bc58364cf8bd5209.png)





还没有评论,来说两句吧...