在Spring框架中,XML配置是最传统和最常见的方式之一,用于管理Bean的创建、依赖注入和生命周期等。这个在Spring中我们使用算是常用的,我们需要根据Spring的基于XML管理Bean了解相关Spring中常用的获取bean的方式、依赖注入值的几种方式等等。
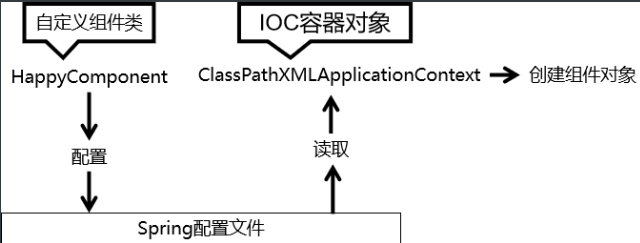
基于XML方式管理bean的流程
- 创建XML配置文件:创建一个XML文件,用于定义Bean的配置信息和依赖关系。可以使用任何文本编辑器创建该文件,通常将其命名为"beans.xml"。
- 声明XML命名空间和模式位置:在XML文件的根元素中,声明Spring的命名空间和模式位置,以便正确解析和验证XML配置。
- 定义Bean:使用元素来定义Bean,指定Bean的ID、类名和其他属性。示例如下:
- 加载XML配置文件:在Java代码中,使用ApplicationContext来加载XML配置文件。示例如下:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); } } - 获取Bean:通过ApplicationContext的getBean()方法,从容器中获取所需的Bean实例。示例如下:
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
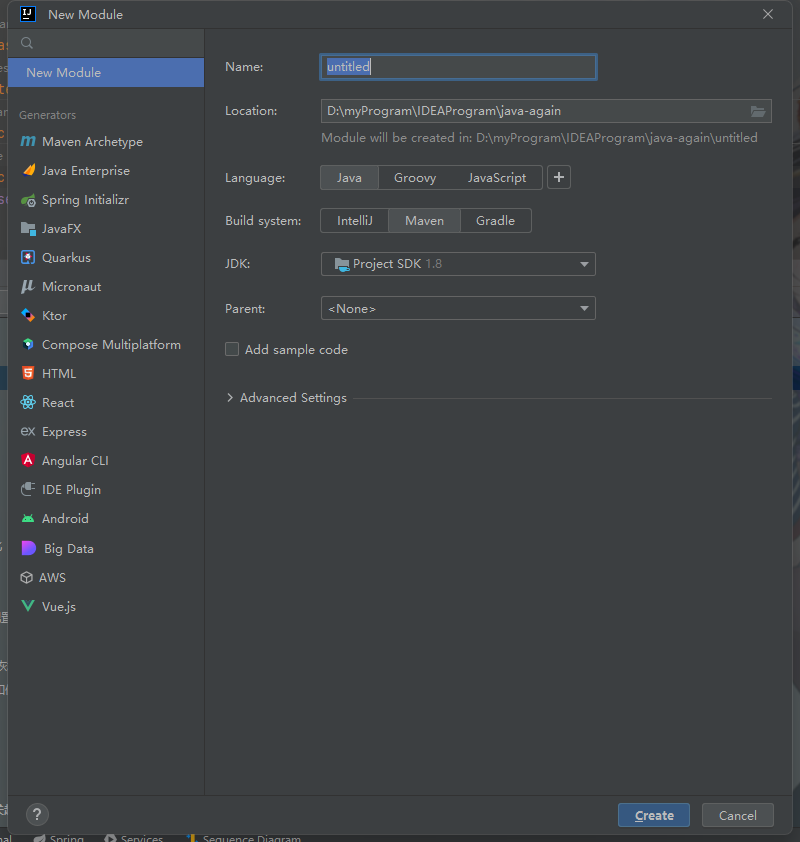
搭建Spring模块结构
创建基本模块并引入相关配置
创建Spring模块
Spring 6 开始已经不在支持javaJDK 8了。
在pom.xml文件中引入相关依赖:
junit junit 4.11 test org.springframework spring-context 5.3.2 mysql mysql-connector-java 8.0.28 com.alibaba druid 1.2.5
创建一个类HelloWorld
public class HelloWorld {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
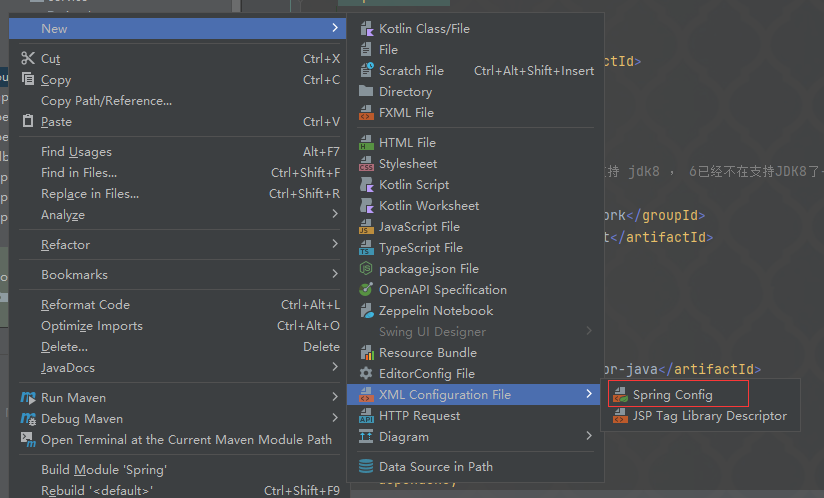
创建一个Spring配置文件
存放到resources目录下
之后我们在创建的配置文件中配置Bean:
接下来我们创建一个测试类
@Test
public void testHelloWorld(){
ApplicationContext ac = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld) ac.getBean("helloworld");
helloworld.sayHello();
}
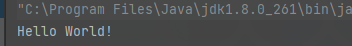
然后我们测试看一下是否输出正常。
大致流程
ps:Spring 底层默认通过反射技术调用组件类的无参构造器来创建组件对象,这一点需要注意。如果在需要无参构造器时,没有无参构造器,则会抛出下面的异常:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name ‘helloworld’ defined in class path resource [applicationContext.xml]: Instantiation of bean failed; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException: Failed to instantiate [com.miaow.spring.bean.HelloWorld]: No default constructor found; nested exception is java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.miaow.spring.bean.HelloWorld.
获取Bean
根据ID获取
由于 id 属性指定了 bean 的唯一标识,所以根据 bean 标签的 id 属性可以精确获取到一个组件对象。
上述例子就是根据id获取一个组件对象。
public void testHelloWorld(){
ApplicationContext ac = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//这个helloworld就是我们在xml配置文件设置的
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld) ac.getBean("helloworld");
helloworld.sayHello();
}
根据类型获取
@Test
public void testHelloWorld(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld bean = ac.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
bean.sayHello();
}
根据id和类型获取
@Test
public void testHelloWorld(){
ApplicationContext ac = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld bean = ac.getBean("helloworld", HelloWorld.class);
bean.sayHello();
}
当根据类型获取bean时,要求IOC容器中指定类型的bean有且只能有一个 。
例如:
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type ‘com.miaow.spring.bean.HelloWorld’ available: expected single matching bean but found 2: helloworldOne,helloworldTwo
- 如果组件类实现了接口,根据接口类型可以获取 bean 吗?
可以,前提是bean唯一
- 如果一个接口有多个实现类,这些实现类都配置了 bean,根据接口类型可以获取 bean 吗?
不行,因为bean不唯一
根据类型来获取bean时,在满足bean唯一性的前提下,其实只是看:『对象 instanceof 指定的类型』的返回结果,只要返回的是true就可以认定为和类型匹配,能够获取到。
Spring依赖注入的方式
Spring的IoC(控制反转)容器通过依赖注入(DI)来管理应用程序中的组件之间的依赖关系。依赖注入是指将一个对象的依赖关系传递给另一个对象,而不是由被依赖对象自己创建或管理依赖对象。Spring框架提供了多种方式来实现依赖注入,包括构造器注入、Setter方法注入、字段注入、注解注入等。
至于字段注入和注解注入我们到Spring注解的时候再继续讲解,这里了解即可。
我们来创建一个学生实体类:
public class Student { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private String sex; public Student() { } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", sex='" + sex + '\'' + '}'; } }setter注入
我们通过Setter方式给上述的Student实体类注入相关值:
我们新建一个springdi.xml配置文件,然后在其中添加如下代码:
接下来我们在测试类方法中测试
@Test public void testDIBySet(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("springdi.xml"); Student studentOne = ac.getBean("studentOne", Student.class); System.out.println(studentOne); }构造器注入
通过构造器注入将依赖项传递给bean
在实体类Student实体类中添加:
public Student(Integer id, String name, Integer age, String sex) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.sex = sex; }之后我们在springdi.xml文件中配置:
注意:
constructor-arg标签还有两个属性可以进一步描述构造器参数:
- index属性:指定参数所在位置的索引(从0开始)
- name属性:指定参数名
测试类中进行测试:
@Test public void testDIBySet(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("springdi.xml"); Student studentOne = ac.getBean("studentTwo", Student.class); System.out.println(studentOne); }特殊值处理赋值
字面符
关于特殊值处理赋值,我们需要事先了解字面符。
什么是字面符?
int a = 10;
声明一个变量a,初始化为10,此时a就不代表字母a了,而是作为一个变量的名字。当我们引用a的时候,我们实际上拿到的值是10。
而如果a是带引号的:‘a’,那么它现在不是一个变量,它就是代表a这个字母本身,这就是字面量。所以字面量没有引申含义,就是我们看到的这个数据本身。
例如
NULL
<(小于) — XML实体
由于在XML中无法直接使用,故而我们需要用XML实体来代替
CDARA节


![[工业自动化-1]:PLC架构与工作原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ce10a1471ed14382bc58364cf8bd5209.png)





还没有评论,来说两句吧...